| Product Includes | Product # | Quantity | Color | Storage Temp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRD4 Rabbit mAb Coated Microwells | 98620 | 96 tests |
|
+4C |
| BRD4 Rabbit Detection mAb | 20320 | 1 ea |
|
+4C |
| HRP Diluent | 13515 | 5.5 ml |
|
+4C |
| TMB Substrate | 7004 | 11 ml |
|
+4C |
| STOP Solution | 7002 | 11 ml |
|
+4C |
| Sealing Tape | 54503 | 2 ea |
|
+4C |
| ELISA Wash Buffer (20X) | 9801 | 25 ml |
|
+4C |
| Cell Lysis Buffer (10X) | 9803 | 15 ml |
|
-20C |
*The microwell plate is supplied as 12 8-well modules - Each module is designed to break apart for 8 tests.
Description
The rapid protocol (RP) PathScan® RP BRD4 Sandwich ELISA Kit is a solid phase sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) that detects endogenous levels of BRD4 protein in a reduced assay time of 1.5 hours. Incubation of cell lysates and detection antibody on the coated microwell plate forms a sandwich with BRD4 protein in a single step. The plate is then extensively washed and TMB reagent is added for signal development. The magnitude of absorbance for the developed color is proportional to the quantity of BRD4 protein. Learn more about your ELISA kit options here.
*Antibodies in this kit are custom formulations specific to kit.
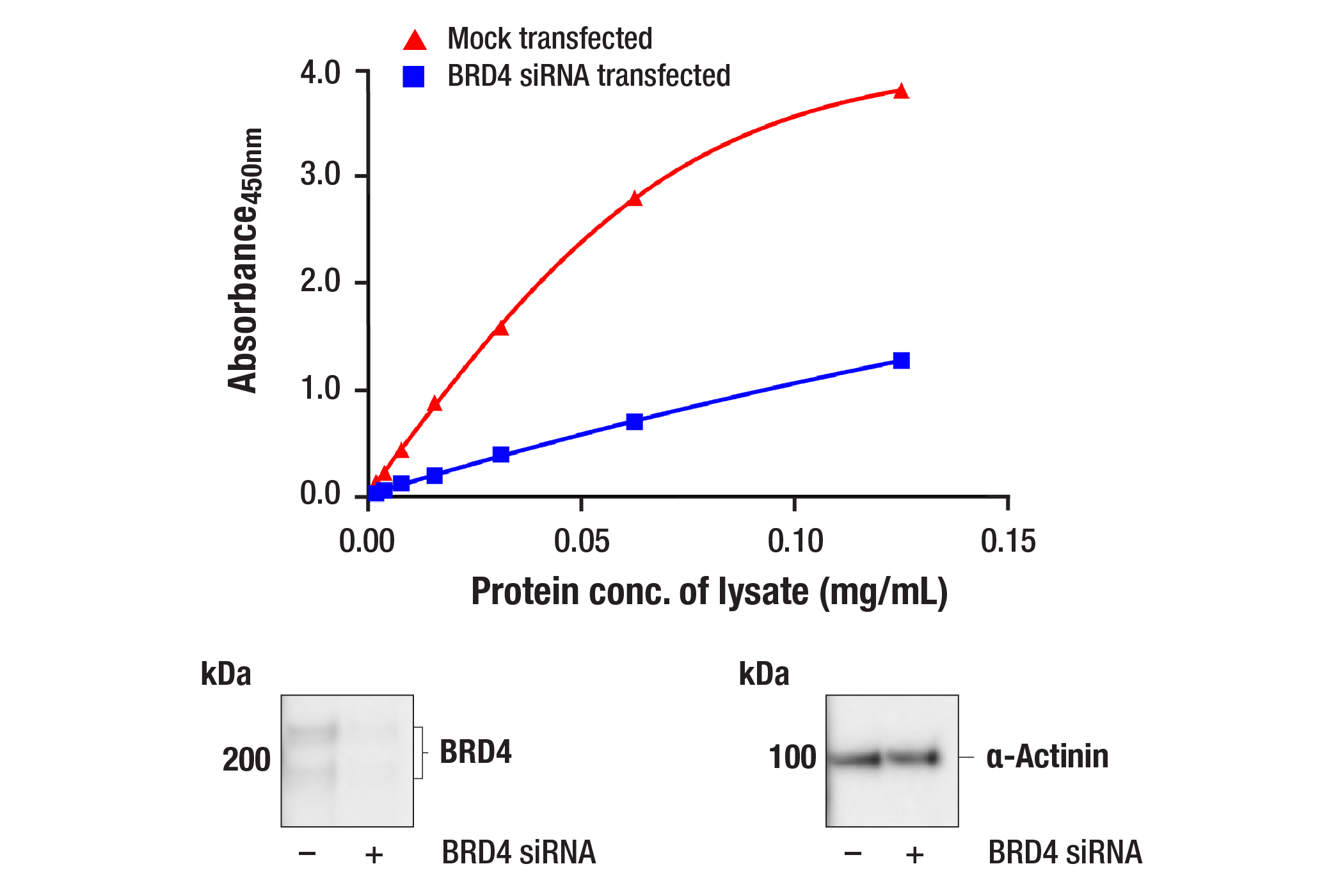
Specificity/Sensitivity
Background
Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) is a member of the bromodomains and extra terminal (BET) family of proteins, which also includes BRD2, BRD3, and BRDT (1-3). BET family proteins contain two tandem bromodomains and an extra terminal (ET) domain, and bind acetyl lysine residues (3). BRD4 is a chromatin-binding protein with a preference for Lys14 on histone H3 as well as Lys5 and Lys12 on histone H4 (4). BRD4 chromatin binding occurs throughout the cell cycle, including condensed mitotic chromosomes, when the majority of genes are silenced (5). BRD4 association with chromatin during mitosis is thought to be an important part of the bookmarking mechanism to accelerate reactivation of the silenced genes upon exit from mitosis (2,6). BRD4 has been shown to facilitate transcription by recruiting the positive transcription elongation factor b (pTEFb) complex that phosphorylates Ser2 of the heptapeptide repeat of the carboxy-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II, promoting transcription elongation (3,7,8). In addition, BRD4 has been found to be part of the super elongation complex and the polymerase associated factor complex (PAFc) in MLL-fusion derived leukemia cell lines, demonstrating a role for BRD4 in the regulation of transcription elongation (9). Research studies have shown that BRD4 (and BET family proteins) may be promising therapeutic targets for various Myc-driven cancers, such as Burkitt’s lymphoma and certain acute myeloid leukemias (1,10,11). Investigators have found molecular inhibition of BET proteins to be effective in inducing apoptosis in various MLL-fusion driven leukemic cell lines by competing BRD3 and BRD4 from chromatin, leading to reduced expression of Bcl-2, Myc, and CDK6 (9). BET inhibition has also been shown to have antitumor activities against nuclear protein in testis (NUT) midline carcinoma cell lines and xenografts in mice where BRD4 is found to be a frequent translocation partner of the NUT protein (12). In addition, BRD4 regulates the expression of some inflammatory genes, and inhibition of BRD4 (and BET family proteins) chromatin binding causes reduced expression of a subset of inflammatory genes in macrophages, leading to protection against endotoxic shock and sepsis (13).
- Belkina, A.C. and Denis, G.V. (2012) Nat Rev Cancer 12, 465-77.
- Voigt, P. and Reinberg, D. (2011) Genome Biol 12, 133.
- Wu, S.Y. and Chiang, C.M. (2007) J Biol Chem 282, 13141-5.
- Dey, A. et al. (2003) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100, 8758-63.
- Dey, A. et al. (2009) Mol Biol Cell 20, 4899-909.
- Zhao, R. et al. (2011) Nat Cell Biol 13, 1295-304.
- Jang, M.K. et al. (2005) Mol Cell 19, 523-34.
- Yang, Z. et al. (2005) Mol Cell 19, 535-45.
- Dawson, M.A. et al. (2011) Nature 478, 529-33.
- Muller, S. et al. (2011) Expert Rev Mol Med 13, e29.
- Mertz, J.A. et al. (2011) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108, 16669-74.
- Filippakopoulos, P. et al. (2010) Nature 468, 1067-73.
- Nicodeme, E. et al. (2010) Nature 468, 1119-23.
Background References
Cross-Reactivity Key
H: human M: mouse R: rat Hm: hamster Mk: monkey Vir: virus Mi: mink C: chicken Dm: D. melanogaster X: Xenopus Z: zebrafish B: bovine Dg: dog Pg: pig Sc: S. cerevisiae Ce: C. elegans Hr: horse GP: Guinea Pig Rab: rabbit All: all species expected
Trademarks and Patents
Limited Uses
Except as otherwise expressly agreed in a writing signed by a legally authorized representative of CST, the following terms apply to Products provided by CST, its affiliates or its distributors. Any Customer's terms and conditions that are in addition to, or different from, those contained herein, unless separately accepted in writing by a legally authorized representative of CST, are rejected and are of no force or effect.
Products are labeled with For Research Use Only or a similar labeling statement and have not been approved, cleared, or licensed by the FDA or other regulatory foreign or domestic entity, for any purpose. Customer shall not use any Product for any diagnostic or therapeutic purpose, or otherwise in any manner that conflicts with its labeling statement. Products sold or licensed by CST are provided for Customer as the end-user and solely for research and development uses. Any use of Product for diagnostic, prophylactic or therapeutic purposes, or any purchase of Product for resale (alone or as a component) or other commercial purpose, requires a separate license from CST. Customer shall (a) not sell, license, loan, donate or otherwise transfer or make available any Product to any third party, whether alone or in combination with other materials, or use the Products to manufacture any commercial products, (b) not copy, modify, reverse engineer, decompile, disassemble or otherwise attempt to discover the underlying structure or technology of the Products, or use the Products for the purpose of developing any products or services that would compete with CST products or services, (c) not alter or remove from the Products any trademarks, trade names, logos, patent or copyright notices or markings, (d) use the Products solely in accordance with CST Product Terms of Sale and any applicable documentation, and (e) comply with any license, terms of service or similar agreement with respect to any third party products or services used by Customer in connection with the Products.