Death Protein Domain
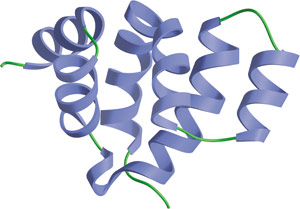
The Death domain from FADD.
Domain Binding and Function
Death domains (DD) are 80–100 residue long motifs involved in apoptotic signal transduction. They are found in both cytoplasmic proteins and in transmembrane proteins, including members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. Death domains serve as recruiting modules as they are able to heterodimerize with the death domains of distinct proteins, including adaptor proteins such as FADD. Due to the significant polarization of charged residues on the surface of the death domain, dimerization may arise primarily through electrostatic interactions. Binding is specific and is thought to arise through complementary charge patterns on dimerization partners.
Structure Reference
- Jeong, E.-J. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274(23), 16337–16342.
Examples of Domain Proteins
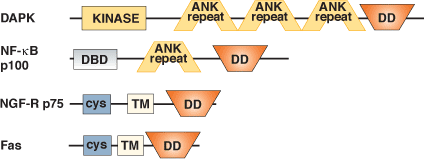
Binding Examples
TNF Receptors | Adaptors | Adaptors | Adaptors |
Fas, TRAIL R1 | FADD | RIP | TRADD |
Fas | RIP | RIP | RAIDD |
TNF-R55 | TRADD | TRADD | FADD |

