EF-Hand Protein Domain
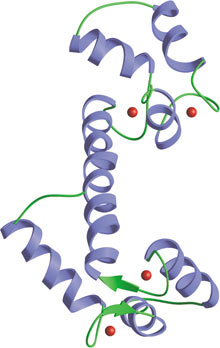
EF-Hand domains in calmodulin from Drosophila melanogaster; calcium atoms in red.
Domain Binding and Function
The EF-hand motif contains approximately 40 residues and is involved in binding intracellular calcium. EF-hand domains are often found in single or multiple pairs, giving rise to various structural/functional variations in proteins containing EF-hand motifs. Proteins containing EF-hands can be grouped into two functional categories—regulatory and structural. The binding of calcium to regulatory EF-hand domain—containing proteins induces a conformational change that is transmitted to their target proteins, often catalyzing enzymatic reactions. In contrast, the binding of calcium to structural EF-hand domain—containing proteins does not induce a significant conformational change. Structural EF-hand domains seem to play a role in buffering intracellular calcium levels.
Structure Reference
- Taylor, D.A. et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266(32), 21375–80.
Examples of Domain Proteins
Binding Examples
EF-Hand Domain Proteins | Binding Partners | Functions |
Calmodulin | Ca2+ | Regulatory proteins |
S-100 | Ca2+ | Regulatory proteins |
Recoverin | Ca2+ | Regulatory proteins |
Calbindin | Ca2+ | Structural proteins |
Parvalbumin | Ca2+ | Structural proteins |

