EH Protein Domain
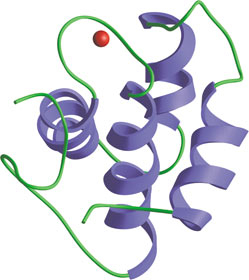
The central EH domain of Eps15.
Domain Binding and Function
The Eps15-Homology (EH) domain is a module of ~100 amino acids originally identified in the tyrosine kinase substrate Eps15. Considerable evidence suggests that EH domain proteins are primarily involved in regulating endocytosis and vesicle transport. EH domains typically recognize peptides with core NPF motifs; proteins containing multiple EH domains may bind cooperatively to proteins with several NPF motifs. EH domain proteins frequently have other repeated motifs (i.e. DPF, PXXP, coiled-coil) and modules (i.e. SH3 domains), suggesting that these proteins may serve a scaffolding function in endocytosis. For example, the DPF motifs of Eps15 interact with the N-terminal appendage region of the clathrin adaptor AP-2 component, α-adaptin. Eps15 and other EH domain proteins (i.e. Intersectin) can bind proteins implicated in endocytosis, such as the GTPase Dynamin and the lipid phosphatase Synaptojanin. Genetic data in yeast have directly demonstrated the importance of an EH domain protein Pan1 in endocytosis.
Structure Reference
- De Beer, T. et al. (1998) Science 281(5381), 1357–1360.
Examples of Domain Proteins
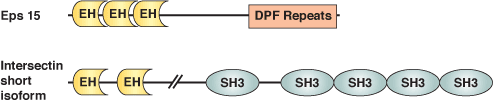
Binding Examples
EH Domain Proteins | Binding Partners |
Eps15 | Epsin, scaffolding protein with ENTH domain |
Eps15 | Synaptojanin, phosphatidylinositol 5'-phosphatase |

