FHA Protein Domain
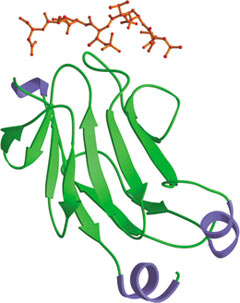
The N-terminal FHA domain of Rad 53p bound to a phospho-threonine peptide (red).
Domain Binding and Function
The Forkhead-Associated (FHA) domain was originally identified as a conserved region from forkhead transcription factors. FHA domains are ~65-100 amino acids long and form a β-sandwich fold consisting of a 3-stranded and a 4-stranded anti-parallel β sheet. While the N- and C terminal ends of the domain are located on adjacent β strands, the opposite side is bound by loops that act to coordinate phosphopeptide binding. FHA domains are found primarily in eukaryotic nuclear proteins that play a role in the DNA-damage response but are also found in certain prokaryotes, including Mycoplasma bacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The FHA domain mediates phosphopeptide interactions with proteins phosphorylated by serine/threonine kinases. Most FHA domains recognize phospho-threonine with specificity provided by residues C-terminal to the phospho-threonine residue, particularly the +3 position. The FHA domains of Rad53 and PNK bind to pTXXD phospho-peptides.
Structure Reference
- Durocher, D. et al. (2000) Mol. Cell 6 (5), 1169–1182.
Examples of Domain Proteins
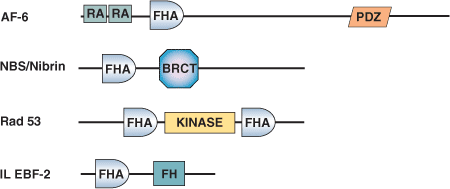
Binding Examples
FHA Domain Proteins | Binding Partners |
KAPP Ser/Thr Phosphatase Kinase | pRLK5 (phosphorylated) Arabidopsis receptor-like Ser/Thr Kinase |
Rad53 S. cerevisiae Ser/Thr Kinase | pRad9 (phosphorylated) S. cerevisiae checkpoint control protein |
MDC1 | ATM, CHK2 Ser/Thr kinases |
Ki67 | hNIFK |
Polynucleotide Kinase (PNK) | XRCC1 and XRCC4 |

