GAT Protein Domain
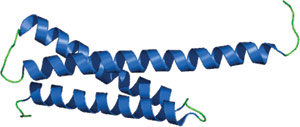
The GAT domain of human GGA1.
Domain Binding and Function
GGA and Tom1 (GAT) domains interact with GTP-bound ARF and are crucial for membrane recruitment of GGAs to the trans-Golgi network. The N-terminal subdomain is important for GAT binding to GTP-bound ARF as the C-terminal subdomain can bind to ubiquitin. The binding of the GAT domain to ubiquitin can be enhanced by the presence of GTP-bound ARF. The GAT domain has structural homology to the SNARE family that contains the same type of three-helix bundle, implicating a role of the GAT domain in membrane fusion. Although GGA1 and GGA3 interact with ARF-GTP and ubiquitin, the functions of GAT in GGA2 and Tom1 are still unclear.
Structure
The N-GAT subdomain or hook subdomain comprises of a helix-loop-helix structure where the N-terminal half of the second long helix α1 is responsible for ARF binding. The C-GAT subdomain constitutes a 3-helix bundle composed of the C-terminal half of α1, α2 and α3. Binding of ubiquitin is mediated by the interaction between residues on one side of α3 helix of the GAT domain and the Ile-44 surface patch of ubiquitin.
Structure Reference
- Suer, S. et al. (2003) PNAS 100(8), 4451–4456.
- Shiba, T. et al. (2003) Nat. Struc. Biol. 10(5), 386–392.
- Shiba, Y. et al. (2004) JBC 279(8), 7105–7111.
Examples of Domain Proteins
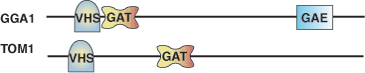
Binding Examples
GAT Domain Proteins | Binding Partners |
GGA1 | ARF1 |
GGA2 | ARF3 |
GGA3 | Rabaptin-5 |
Tom1 |
|

