LIM Protein Domain

C-terminal LIM domain from quail CRP2.
Domain Binding and Function
The LIM domain was first identified in the developmentally regulated transcription factors Lin-1, Isl-1, and Mec-3. The approximately 60 amino acid long domain has been identified in over 300 proteins from organisms ranging from yeast to human. The LIM domain is a zinc-binding, cysteine-rich motif consisting of two tandemly repeated zinc fingers. The classic LIM consensus sequence includes a CX2CX16 - 23HX2CX2CX2CX16 - 21 CX2(CH/D) sequence associated with a highly variable sequence in the remainder of the domain that confers functional specificity. Unlike GATA type zinc fingers, LIM domains mediate protein-protein interactions rather than directly bind DNA. LIM domain containing proteins have functionally diverse cellular roles as regulators of gene expression, cell adhesion, cell motility and signal transduction. Some LIM-domain containing proteins function as adapters to promote protein complex (i.e. LMO and CRP) formation while other LIM proteins have functions conferred by the presence of additional functional domains (i.e. DNA binding homeodomain, catalytic kinase domain). In addition, certain LIM domains can form homodimers with other LIM domains.
Structure Reference
- Konrat, R. et al. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272(18), 12001–12007.
Examples of Domain Proteins
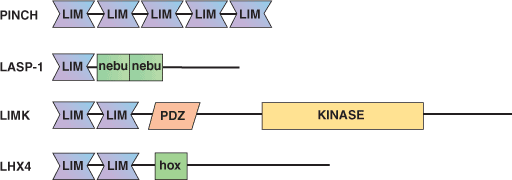
Binding Examples
LIM Domain Proteins | Binding Partners |
Enigma | Insulin receptor (3rd LIM domain) |
Enigma | Ret receptor (2nd LIM domain) |
PINCH | Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) (1st LIM domain) |
PINCH | NCK2 (4th LIM Domain) |
hCRP | hCRP homo-dimerization |

