LRR Protein Domain
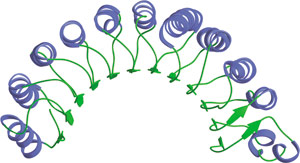
Leucine-Rich Repeats in Rna1p.
Domain Binding and Function
Leucine-Rich Repeats (LRR) are 22–28 amino acid motifs found in a number of proteins with diverse functions and cellular locations. These repeats are usually involved in protein—protein interactions; when acting serially they form nonglobular, crescent-shaped structures. The crescent shape adopted by a series of leucine-rich repeats creates a solvent-exposed, elongated, concave surface of parallel β-strands that act as a scaffold for protein—protein interactions. Different residues arranged in an appropriate orientation on the surface of the structurally conserved three-dimensional fold specify the particular function of each LRR crescent. For example, RNAse inhibitor and U2A' LRR scaffolds interact with their targets via the concave inner surface of the crescent, while in S. pombe Rna1p the Ran binding site is located on the side face of the crescent within the loop regions connecting the β-strands and α-helices.
Structure Reference
- Hillig, R.C. et al. (1999) Mol. Cell 3(6), 781–791.
Examples of Domain Proteins

Binding Examples
FHA Domain Proteins | Binding Partners |
RNAse Inhibitor | RNAse |
Rna1p | RAN small GTPase |
TAP | Constitutive transport element (CTE) of retroviral RNAs |
U2A' | Ribonucleoprotein domain of U2B' |
CIITA | MHC class II promoter binding complex |

