PAS Protein Domain
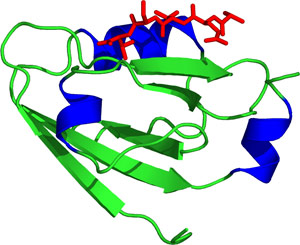
The PAS domain of HIF-2α.
Domain Binding and Function
PAS (Per ARNT Sim) domains, first identified in Drosophila proteins PER and ARNT, are modules found in proteins from organisms across all taxa. PAS domains play important roles as sensory modules for oxygen tension, redox potential or light intensity. In response to stimuli, the domain either mediates protein-protein interactions or binds cofactors within their hydrophobic cores to regulate protein-protein interactions. In response to hypoxic conditions, the HIFα PAS-B domain heterodimerizes with PAS-B of ARNT, which is involved in transcriptional activation by the basic helix-loop-helix. The PAS domain of the serine/threonine kinase PASK acts as a regulatory sensor that has a compound and ligand-binding region that initiates a switch that regulates kinase activity.
Structure
The PAS domain consists of a conserved α/β-fold that lacks an obviously conserved amino acid sequence. The PAS common fold is characterized by several α-helices flanking a five-stranding anti-parallel β-sheet that share a few residues to form part of a conserved hydrophobic core located around αA. Loops at the αA/αB segment are important for ligand binding.
Structure Reference
- Erbel, P.J. et al. (2003) PNAS. 100(26), 15504–15509.
- Amezcua, C.A. et al. (2002) Structure 10, 1349–1361.
Examples of Domain Proteins

Binding Examples
PAS Domain Proteins | Binding Partners |
HIFα |
|
ARNT (HIFβ) |
|
PASK |
|
HERG |
|
NCoA-1 | STAT6, LXXLL |

