PUF (Pumilio) Protein Domain
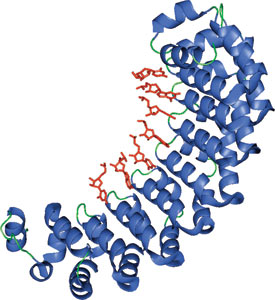
The PUF domain of Pumilio bound to RNA (red).
Domain Binding and Function
The PUF family of proteins is highly conserved among organisms from yeast to humans and plants. All Pumilio/PUF proteins contain a C-terminal domain that consist of eight repeated sequence subunits with N- and C-terminal flanking regions termed the Pumilio homology domain. Pumulio repeat proteins regulate various aspects of development by controlling mRNA stability and translation through its sequence-specific interaction with the 3' untranslated region of target mRNAs. The affinity and specificity of the interaction of this domain and RNA is determined by the reiterated use of the individual Pumilio subunits that make contact with the RNA base using three conserved amino acid residues that contact individual RNA bases.
Structure
The structure shown is of the Human Pumilio (PUF) domain-containing protein, Pumilio1, in complex with RNA. The eight pumilio repeats bind RNA using the concave surface of the protein. Structurally, these domains are α-helical repeat proteins that resemble the Armadillo (ARM) repeat proteins, β-catenin and karyopherin α.
Structure Reference
- Wang, X. et al. (2002) Cell 110(4), 501–512.
Examples of Domain Proteins


