UBA Protein Domain
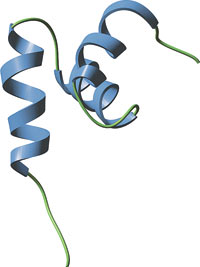
The internal UBA domain of HHR23A.
Domain Binding and Function
The Ubiquitin-Associated (UBA) domain is an approximately 40 amino acid motif that was first recognized in proteins associated with ubiquitination, and later seen in proteins involved in DNA nucleotide excision-repair. UBA domains bind mono-, di-, tri-, and tetra-ubiquitin in vitro but appear to bind to polyubiquitin with a higher affinity, suggesting that polyubiquitinated proteins are in vivo UBA domain protein binding substrates. A number of UBA domains form homodimers and heterodimerize with other substrates. Functionally, proteins with UBA domains are thought to limit ubiquitin chain elongation and to target ubiquitinated proteins to the 26S proteasome for degradation.
Structure
NMR data reveals that the UBA domains of the human homologue of yeast Rad23A (HHR23A) form three-helix bundles with a hydrophobic core that stabilizes the protein. These domains also possess a conserved surface patch of hydrophobic amino acids that likely interact with hydrophobic regions of ubiquitin and other target proteins.
Structure Reference
- Mueller, T.D. and Feigon, J. (2002) J. Mol. Biol. 319 (5), 1243–1255.
Examples of Domain Proteins
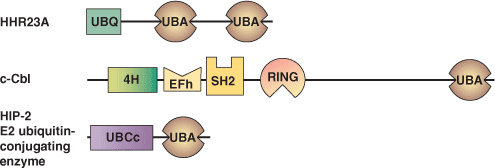
Binding Examples
UBA Domain Proteins | Binding Partners |
HHR23A | mono and polyubiquitin |
c-Cbl | unknown |
HIP-2 E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme | unknown |

