Common Pluripotency Markers
Pluripotency is the ability of a cell to differentiate into any cell type. The ability to induce pluripotency in cells from an individual provides a valuable tool for developmental biology studies and disease research studies, and could ultimately be applied to personalized stem cell therapy. Cell Signaling Technology (CST) offers a comprehensive line of stem cell and lineage markers. CST™ antibodies are extensively validated in relevant research applications by our team of in-house experts and validation data is presented online for each product. And our technical support scientists are available for consultation, just in case you need a partner at the bench.
Reprogramming Factors Key: O—Oct4, K—Klf4, S—Sox2, M—c-Myc, E—Esrrb, Nr—Nr5a2, C—C/EBPα, L—Lin28, N—Nanog
| Species | Cell Type | Reprogramming Factors | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mouse | Fibroblasts | OKSM, OKS, OSE, KSNr | Takahashi & Yamanaka 2006 |
| Mature B & T cells | OKSMC, OKSM | Hanna et al. 2008; Eminli et al. 2009 | |
| Myeloid progenitors | OKSM | Eminli et al. 2009 | |
| Hematopoietic stem cells | OKSM | Eminli et al. 2009 | |
| Adipose-derived stem cells | OKSM | Sugii et al. 2010 | |
| Dermal Papilla | OKM, OK | Tsai et al. 2010 | |
| Satellite cells | OKSM | Tan et al. 2011 | |
| Pancreatic β-cells | OKSM | Stadtfeld et al. 2008 | |
| Hepatic endoderm | OKS | Aoi et al. 2008 | |
| Neural stem cells | OK | Kim et al. 2008; Kim et al. 2009 | |
| Melanocytes | OKM | Utikal et al. 2009 | |
| Human | Fibroblasts | OKSM, OSLN, OKS | Takahashi et al. 2007; Yu et al. 2007; Nakagawa et al. 2008 |
| Mobilized peripheral blood | OKSM | Loh et al. 2009 | |
| Cord blood endothelia | OSLN | Haase et al. 2009 | |
| Cord blood stem cells | OKSM, OS | Eminli et al. 2009; Giorgetti et al. 2009 | |
| Adipose-derived stem cells | OKSM, OKS | Sugii et al. 2010; Aoki et al. 2010 | |
| Hepatocytes | OKSM | Liu et al. 2010 | |
| Keratinocytes | OKSM, OKS | Aasen et al. 2008 | |
| Neural stem cells | O | Kim et al. 2009 | |
| Pancreatic β-cells | OKSM | Bar-Nur et al. 2011 | |
| Amniotic cells | OKSM, OSN | Li et al. 2009; Zhao et al. 2010 |
Table adapted from Stadtfeld and Hochedlinger 2011.
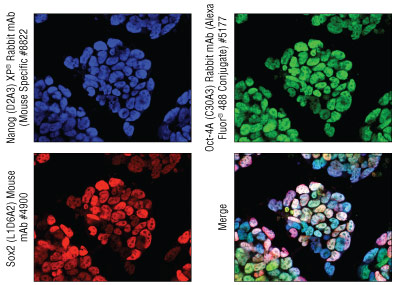
Immunofluorescent analysis of mouse iPS Cells
Transcription factor expressed in undifferentiated pluripotent embryonic stem cells and germ cells during normal development. Together with Sox2 and Nanog, is necessary for the maintenance of pluripotent potential.
Transcription factor expressed in undifferentiated pluripotent embryonic stem cells and germ cells during development. Together with Oct-4 and Nanog, is necessary for the maintenance of pluripotent potential.
Homeodomain-containing transcription factor essential for maintenance of pluripotency and self renewal in embryonic stem cells. Expression is controlled by a network of factors including Sox2 and the key pluripotency regulator Oct-4.
Zinc-finger-containing transcription factor Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4); used for generation of human and mouse ES cells.
Present on the surface of human stem, teratocarcinoma, and embryonic germ cells.
Lactoseries oligosaccharide expressed on the surface of mouse embryonic carcinoma, embryonic stem, and germ cells, but only expressed on human germ cells. Expression of SSEA1 on human cells increases upon differentiation, while differentiation of mouse cells leads to decreased expression.
Glycolipid carbohydrate expressed on the surface of human teratocarcinoma stem, embryonic germ, and embryonic stem cells. Expression of human SSEA4 decreases following differentiation of human embryonic carcinoma cells, but increases following differentiation in mouse cells.