CH Protein Domain
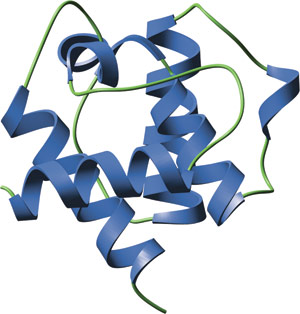
The CH domain of β-spectrin.
Domain Binding and Function
The Calponin Homology (CH) domain is a protein module of approximately 110 amino acids present in cytoskeletal and signal transduction proteins. Two CH domains in tandem form an F-actin binding region at the N-terminus of spectrin-like proteins such as dystrophin and α-actinin. Such tandem CH domains bind F-actin with 5 - 50 µM affinity and cross-link actin filaments into bundles and networks. CH domains can be subdivided into at least three types. Type 1 and 2 CH domains are found together in tandem in cytoskeletal proteins such as dystrophin, spectrin and filamin. Type 3 CH domains are found in proteins that regulate muscle contraction (i.e. calponin) and in signaling proteins (i.e. Vav, ARHGEF6 and IQGAP). Type 3 CH domains may not interact directly with actin, but rather act as regulatory domains or protein-protein interaction scaffolds to modulate the activity of proteins in which they are present.
Structure
The CH domain consists four main α-helices connected by either long loop regions or two to three shorter helices. Three dominant helices form a parallel bundle against which the N-terminal helix packs at a right angle. Two CH domains in tandem pack such that the C-terminal helix of the first domain connects the two domains to create a single compact fold.
Structure Reference
- Banuelos, S. et al. (1998) Structure 6(11), 1419–1431.
Examples of Domain Proteins
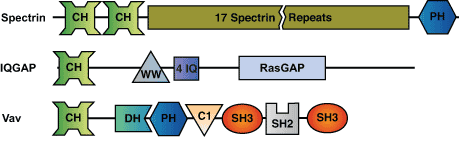
Binding Examples
CH Domain Proteins | Binding Partners |
β-spectrin | F-actin |
Fimbrin | F-actin |
Dystrophin | F-actin |
