GRAM Protein Domain
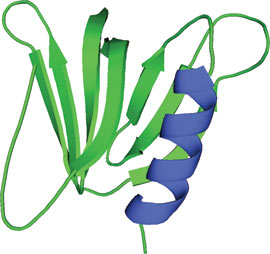
The GRAM domain of MTMR2.
Domain Binding and Function
The GRAM (Glucosyltransferases, Rab-like GTPase activators and Myotubularins) domain is approximately 70 amino acids in length and consists of a 7-stranded β sandwich and a C-terminal α-helix. GRAM domains are commonly found in myotubularin family phosphatases and are thought to occur in ~180 proteins. The GRAM domain of the myotubularin related protein 2 (MTMR2) shows an unexpectedly large fold similar to that found in the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. Proteins containing GRAM domains are predominately involved in membrane-coupled processes. Functional studies demonstrate that the GRAM domain is involved in PI-(3,5)P2 substrate recognition, PI-(3)-P/PI-(5)-P dependent oligomerization and PI-(5)-P specific allosteric activation of myotubularin phosphatases. Corresponding gene mutations affecting GRAM domain structure can lead to human disorders including X-linked congenital myopathy.
Structure
The MTMR2 GRAM sequence forms five β strands that are part of a larger motif that structurally adopts a PH domain fold. The GRAM domain along with immediately adjacent amino acid residues form a tertiary structure that consists of a 7-stranded β sandwich with a C-terminal α-helix. The structure of the MTMR2 GRAM domain is very similar to the pleckstrin PH domain; given highly conserved residues among GRAM core domains, other GRAM domains would likely share similar PH domain folds.
Structure Reference
- Begley, M.J., et al. (2003) Mol. Cell 12(6), 1391–1402.
Examples of Domain Proteins
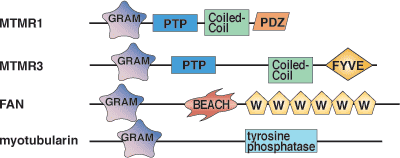
Binding Examples
Gram domain protein | Specific Phosphoinositide ligands |
MTMR2 | PI-(3,5)-P2, PI-(5)-P |
MTM1, MTMR3, and MTMR6 | PI-(5)-P |
