PH Protein Domain
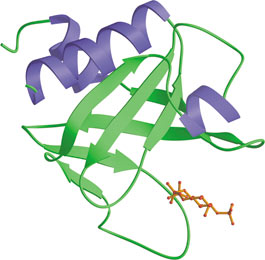
The PH domain from rat PLC δ1 bound to Ins(1,4,5)P3 (red).
Domain Binding and Function
Pleckstrin-homology (PH) domains are structurally well-characterized modules of ~120 amino acids found in a wide variety of signaling proteins involved intracellular trafficking, cellular signaling and cytoskeletal remodeling. The human proteome contains some 250 PH domains, all of which share a common core fold consisting of a 7-stranded β-sandwich formed from two near-orthogonal β-sheets. The basic residues in the β1/β2 loop of the PH domain form a well-defined binding site with the phosphates of phosphoionositide headgroups. Some PH domains bind with high affinity (low µM or nM Kd) to specific phosphoinositides such as phosphatidylinositol- 4,5-bisphosphate, PI-3, 4-P2 or PI-3,4,5-P3. Binding to phosphoinositides may allow PH proteins to respond to lipid messengers by localizing to membranes and transmitting signals to downstream targets.
Structure Reference
- Ferguson, K.M. et al. (1995) Cell 83(6), 1037–1046.
Examples of Domain Proteins
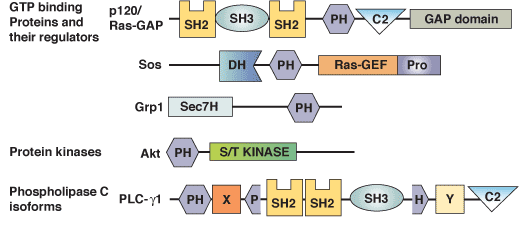
Binding Examples
PH Domain Proteins | Specific Phosphoinositide Ligand |
Phospholipase C-δ; mSos1, RasGAP; Tsk, pleckstrin | PI-(4,5)-P2 |
Btk; Grp1 | PI-(3,4,5)-P3 |
Akt; DAPP1; TAPP1 | PI-(3,4)-P2 |
