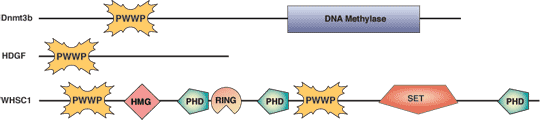
PWWP Protein Domain
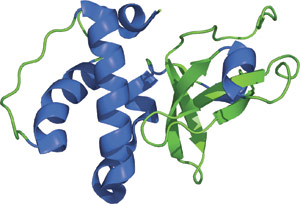
PWWP Domain of Mammalian Dnmt3b.
Domain Binding and Function
The PWWP domain was first identified from a gene located in the Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome (WHS) critical region. The translocated form of WHSC1 is involved in lymphoid Multiple Myeloma (MM) disease, also known as plasmacytoma. The identified domain was designated PWWP based on its central core residues of proline-tryptophan-tryptophan-proline. The ~135 amino acid PWWP domain is found in eukaryotic proteins from yeast to mammals, including approximately two-dozen human proteins. The N-terminal half of the PWWP domain exhibits a barrel-like five-stranded structure that resembles the SAND domain, while the C-terminal portion is made up of a five-helix bundle. PWWP domains are involved in DNA methylation, DNA repair and regulation of transcription. The PWWP domain of Dnmt3b2 contains a basic surface that may play a role in DNA binding.
Structure Reference
- Qiu, C. et al. (2002) Nature Struct. Biology 9(3) 217–224.
Examples of Domain Proteins