TUBBY Protein Domain
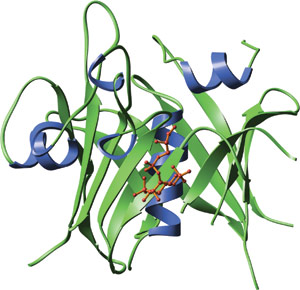
The carboxy-terminal domain of mouse tubby bound to GPMI-p2 (red), an analog of the head group of PI(4,5)P2.
Domain Binding and Function
The TUBBY domain was first identified in the TUBBY protein that is implicated in mature-onset obesity. Spanning approximately 260 amino acids in length, the dual binding TUBBY domain interacts with both DNA and phosphotidylinositol. The TUBBY domain of the TUBBY and TULP proteins binds with high specificity to biphosphorylated phosphoinositides that are phosphorylated at the 4-position on the inositol ring (such as PI(4,5)P2). This allows the TUBBY domain to function downstream of receptors such as the 5HT2C serotonin receptor. 5HT2C activation leads to stimulation of trimeric G-proteins that activate phospholipase C (PLC). PLC hydrolysis of PI(4,5)P2 releases the TUBBY domain from the membrane, allowing nuclear translocation. Once in the nucleus, the TUBBY domain binds DNA and the TUBBY protein amino-terminal transcription factor-like activation domain promotes transcription.
Structure
The TUBBY domain forms an unusual helix-filled β-barrel structure. A co-crystal of the TUBBY domain in complex with GPMI-P2, an analog of the head group from phosphotidylinositol (4,5) biphosphate, reveals that phosphoinositide binding occurs in a basic pocket at one end of the putative DNA binding groove. Amino acid side chains involved in interactions with GMPI-P2 are primarily in β-strands 4, 5 and 6 and helix 6A. A central feature of the binding interface is the Lysine-330 that coordinates between the 4- and 5- position phosphates and provides high selectivity for phosphatidyl inositides that are phosphorylated on adjacent positions of the inositol ring.
Structure Reference
- Santagata, S. et al. (2001), Science 292(5524), 2041–2050.
Examples of Domain Proteins
Binding Examples
TUBBY Domain Proteins | Binding Partners |
Tubby | PI(4,5)P2; PI(3,4)P2 |
