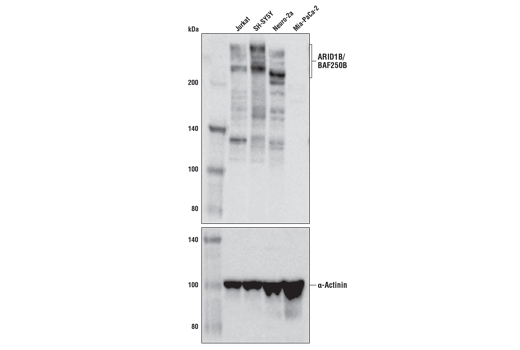
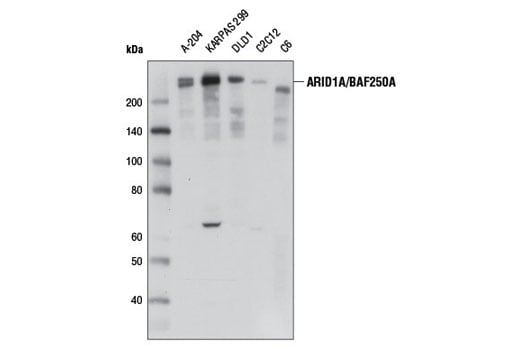
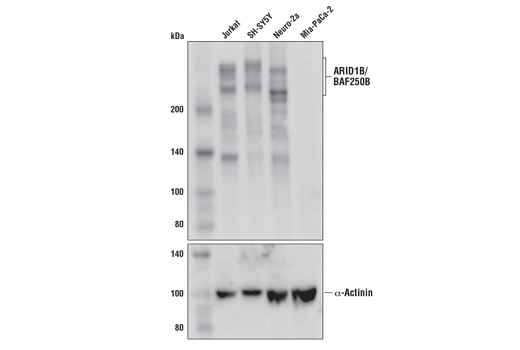
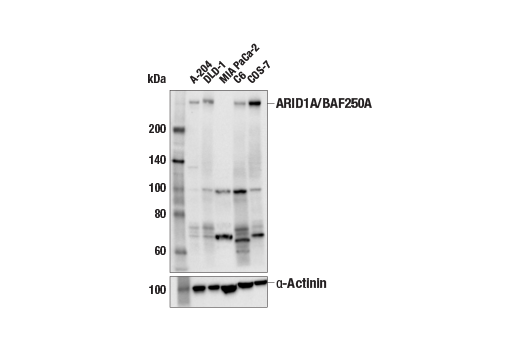
ARID1B/BAF250B (E9J4T) Rabbit mAb #92964
- WB
- IP
- ChIP
To Purchase # 92964
| Cat. # | Size | Qty. | Price | Ships |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 92964T | 20 µl | $153 | ||
| 92964S | 100 µl | $339 |
Supporting Data
| REACTIVITY | H M |
| SENSITIVITY | Endogenous |
| MW (kDa) | 250, 280 |
| Source/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
Application Key:
- WB-Western Blotting
- IP-Immunoprecipitation
- ChIP-Chromatin Immunoprecipitation
Species Cross-Reactivity Key:
- H-Human
- M-Mouse
- Related Products
Product Information
Product Usage Information
For optimal ChIP and ChIP-seq results, use 10 μl of antibody and 10 μg of chromatin (approximately 4 × 10^6 cells) per IP. This antibody has been validated using SimpleChIP® Enzymatic Chromatin IP Kits.
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
| Simple Western™ | 1:10 - 1:50 |
| Immunoprecipitation | 1:200 |
| Chromatin IP | 1:50 |
| Chromatin IP-seq | 1:50 |
Storage
Protocol
Specificity / Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
Source / Purification
Background
ARID1B (A-T rich interacting domain 1B), also known as BAF250B, is a DNA-binding member of the SWI/SNF complex. It has 60% homology with ARID1A/BAF250A, and the proteins are mutually exclusive members of the complex, akin to Brg1 and BRM (10). ARID1B plays a role in synapse formation and dendritic arborization in neuronal development, and haploinsufficiency of ARID1B has been reported in intellectual disability (11-13). Mutations in ARID1B have also been shown in Coffin-Siris syndrome (14). ARID1B/BAF250B is a critical vulnerability in ARID1A/BAF250A mutant cancers, and could be explored as a potential therapeutic target (15).
- Ho, L. and Crabtree, G.R. (2010) Nature 463, 474-84.
- Becker, P.B. and Hörz, W. (2002) Annu Rev Biochem 71, 247-73.
- Eberharter, A. and Becker, P.B. (2004) J Cell Sci 117, 3707-11.
- Bowman, G.D. (2010) Curr Opin Struct Biol 20, 73-81.
- Gangaraju, V.K. and Bartholomew, B. (2007) Mutat Res 618, 3-17.
- Lessard, J.A. and Crabtree, G.R. (2010) Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 26, 503-32.
- Morettini, S. et al. (2008) Front Biosci 13, 5522-32.
- Wolf, I.M. et al. (2008) J Cell Biochem 104, 1580-6.
- Simone, C. (2006) J Cell Physiol 207, 309-14.
- Wang, X. et al. (2004) Biochem J 383, 319-25.
- Ka, M. et al. (2016) J Neurosci 36, 2723-42.
- Halgren, C. et al. (2012) Clin Genet 82, 248-55.
- Hoyer, J. et al. (2012) Am J Hum Genet 90, 565-72.
- Tsurusaki, Y. et al. (2012) Nat Genet 44, 376-8.
- Helming, K.C. et al. (2014) Nat Med 20, 251-4.
Limited Uses
Except as otherwise expressly agreed in a writing signed by a legally authorized representative of CST, the following terms apply to Products provided by CST, its affiliates or its distributors. Any Customer's terms and conditions that are in addition to, or different from, those contained herein, unless separately accepted in writing by a legally authorized representative of CST, are rejected and are of no force or effect.
Products are labeled with For Research Use Only or a similar labeling statement and have not been approved, cleared, or licensed by the FDA or other regulatory foreign or domestic entity, for any purpose. Customer shall not use any Product for any diagnostic or therapeutic purpose, or otherwise in any manner that conflicts with its labeling statement. Products sold or licensed by CST are provided for Customer as the end-user and solely for research and development uses. Any use of Product for diagnostic, prophylactic or therapeutic purposes, or any purchase of Product for resale (alone or as a component) or other commercial purpose, requires a separate license from CST. Customer shall (a) not sell, license, loan, donate or otherwise transfer or make available any Product to any third party, whether alone or in combination with other materials, or use the Products to manufacture any commercial products, (b) not copy, modify, reverse engineer, decompile, disassemble or otherwise attempt to discover the underlying structure or technology of the Products, or use the Products for the purpose of developing any products or services that would compete with CST products or services, (c) not alter or remove from the Products any trademarks, trade names, logos, patent or copyright notices or markings, (d) use the Products solely in accordance with CST Product Terms of Sale and any applicable documentation, and (e) comply with any license, terms of service or similar agreement with respect to any third party products or services used by Customer in connection with the Products.