Reptin/RuvBL2 Antibody #8959
- WB
To Purchase # 8959
| Cat. # | Size | Qty. | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8959S | 100 µl | $306 |
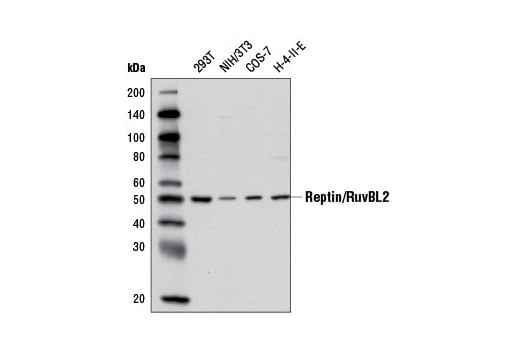
Supporting Data
| REACTIVITY | H M R Mk |
| SENSITIVITY | Endogenous |
| MW (kDa) | 48 |
| SOURCE | Rabbit |
Application Key:
- WB-Western Blotting
Species Cross-Reactivity Key:
- H-Human
- M-Mouse
- R-Rat
- Mk-Monkey
- Related Products
Product Information
Product Usage Information
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blotting | 1:1000 |
Storage
Protocol
Specificity / Sensitivity
Species Reactivity:
The antigen sequence used to produce this antibody shares 100% sequence homology with the species listed here, but reactivity has not been tested or confirmed to work by CST. Use of this product with these species is not covered under our Product Performance Guarantee.
Species predicted to react based on 100% sequence homology:
Source / Purification
Background
Reptin also plays a role in modulating cellular responses to hypoxia. Hypoxia induced methylation of Reptin by the methyltransferase G9a leads to its recruitment to hypoxia responsive promoters where it negatively regulates transcription of these genes (8). In addition to transcriptional regulatory roles, Reptin also participates in the telomerase biogenesis processes as part of the telomerase complex and in DNA damage response as part of the TIP60 acetyltransferase complex that stimulates ATM kinase activity necessary for phosphorylation of proteins involved in both checkpoint activation and DNA repair (9,10).
- Jha, S. and Dutta, A. (2009) Mol Cell 34, 521-33.
- Gallant, P. (2007) Trends Cell Biol 17, 187-92.
- Huber, O. et al. (2008) Cancer Res 68, 6873-6.
- Kim, J.H. et al. (2005) Nature 434, 921-6.
- Bauer, A. et al. (2000) EMBO J 19, 6121-30.
- Wood, M.A. et al. (2000) Mol Cell 5, 321-30.
- Dugan, K.A. et al. (2002) Oncogene 21, 5835-43.
- Lee, J.S. et al. (2010) Mol Cell 39, 71-85.
- Venteicher, A.S. et al. (2008) Cell 132, 945-57.
- Sun, Y. et al. (2010) Cell Cycle 9, 930-6.
Limited Uses
Except as otherwise expressly agreed in a writing signed by a legally authorized representative of CST, the following terms apply to Products provided by CST, its affiliates or its distributors. Any Customer's terms and conditions that are in addition to, or different from, those contained herein, unless separately accepted in writing by a legally authorized representative of CST, are rejected and are of no force or effect.
Products are labeled with For Research Use Only or a similar labeling statement and have not been approved, cleared, or licensed by the FDA or other regulatory foreign or domestic entity, for any purpose. Customer shall not use any Product for any diagnostic or therapeutic purpose, or otherwise in any manner that conflicts with its labeling statement. Products sold or licensed by CST are provided for Customer as the end-user and solely for research and development uses. Any use of Product for diagnostic, prophylactic or therapeutic purposes, or any purchase of Product for resale (alone or as a component) or other commercial purpose, requires a separate license from CST. Customer shall (a) not sell, license, loan, donate or otherwise transfer or make available any Product to any third party, whether alone or in combination with other materials, or use the Products to manufacture any commercial products, (b) not copy, modify, reverse engineer, decompile, disassemble or otherwise attempt to discover the underlying structure or technology of the Products, or use the Products for the purpose of developing any products or services that would compete with CST products or services, (c) not alter or remove from the Products any trademarks, trade names, logos, patent or copyright notices or markings, (d) use the Products solely in accordance with CST Product Terms of Sale and any applicable documentation, and (e) comply with any license, terms of service or similar agreement with respect to any third party products or services used by Customer in connection with the Products.

