MethylScan® - Methylation Proteomics
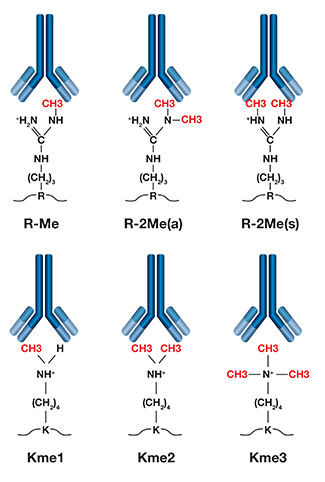
Representation of different methylation antibodies and their target modifications.
Protein methylation is a common post-translational modification (PTM) that mostly occurs on arginine and lysine residues. Arginine methylation regulates processes such as RNA processing, gene transcription, DNA damage repair, protein translocation, and signal transduction. Lysine methylation is best known to regulate histone function and is involved in epigenetic regulation of gene transcription.
MethylScan® technology for methylation proteomics uses proprietary methyl-arginine (Me-R) or methyl-lysine (Me-K) antibodies to enrich methyl-containing peptides from protease digested samples. Methylation antibodies from CST are rigorously tested, including in peptide blocking experiments and peptide arrays to confirm specificity and sensitivity. Each of these reagents is each optimally designed and formulated to recognize only its respective form of methylated arginine and lysine residue.
View a publication demonstrating MethylScan® methylation proteomics.
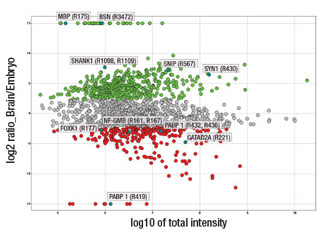
Quantitative analysis of arginine monomethylation in mouse brain and embryo: Each dot in the scatter plot represents a unique arginine monomethylated peptide identified using PTMScan® Mono-Methyl Arginine Motif [mme-RG] Kit #12235. The x-axis is the log10 value of the total intensity of the representative peptide for a methylation site in mouse brain and embryo, and the y-axis shows the log2 ratio of intensity of the peptide in mouse brain vs. embryo. A cutoff of 5-fold was set to indicate increased arginine monomethylation peptide abundance in either brain (green dots) or embryo (red dots). For the methyl peptides that uniquely existed in a specific tissue, arbitrary log2 ratios of 15 (brain specific) and -15 (embryo specific) were assigned. Several representative enriched brain and embryo proteins are highlighted on the graph.