UbiScan® - Ubiquitination Proteomics
Protein ubiquitination is involved in many cellular processes including proteasomal degradation, endocytosis, DNA repair, cell cycle regulation, and gene expression. Abnormal ubiquitination is involved in diseases such as cancer, neurodegeneration, and metabolic syndrome.
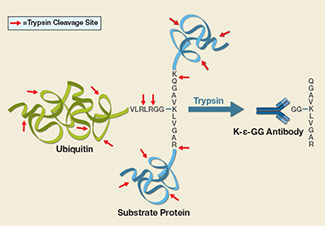
UbiScan® technology for ubiquitination proteomics employs a proprietary antibody against the di-glycine (K-ε-GG) remnant that is left on ubiquitinated lysine residues after trypsin digestion. This ubiquitin remnant motif antibody is used to enrich ubiquitinated peptides from trypsin digested samples prior to LC-MS/MS analysis for quantitative profiling of thousands of non-redundant ubiquitinated sequences. (Other ubiquitin-like modifiers also leave K-ε-GG remnants, for example NEDD8 and ISG15.)
View webinar to see an example of how PTMScan technology using the K-ε-GG remnant motif antibody can be applied in large-scale quantitative analysis of the ubiquitylome.