B Cells differentiate from hematopoietic cells found in the bone marrow. Immunoglobulin (Ig) receptors are assembled on the surface of B Cells and allow for specific recognition of a single antigen. Varying gene rearrangements during development lead to the differential expression of Ig surface receptors. Mature B Cells migrate to the lymph nodes and spleen after which they can further become memory B Cells or plasma cells.
While T Cells and B Cells are both able to recognize pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and apoptotic cells, there two cell types are distinct in their characteristics and functions. B Cells develop in the bone marrow while T Cells are formed in the thymus.
The main difference is that T Cells can only recognize viral antigens outside the infected cells whereas B Cells can recognize the surface antigens of bacteria and viruses, which in turn results in antibody production.
The critical cells that mediate antibody production are B Cells. Specific B cell receptors recognize and facilitate processing of antigens. B Cell activation occurs with help from T Cells, allowing the B Cells to mature into plasma cells that secrete antibodies.
The B Cell receptor (BCR) binds antigens, resulting in activation of multiple signaling cascades that involve kinases, GTPases, and transcription factors. This results in changes in cell metabolism, gene expression, and cytoskeletal organization. The complexity of BCR signaling permits many distinct outcomes including survival, apoptosis, proliferation, or differentiation into plasma cells or memory B Cells.
CST has a wide array of expertly validated antibodies that can distinguish B cell populations accurately and reproducibly by WB, IF/IHC, IP and extracellular/intracellular flow cytometry.
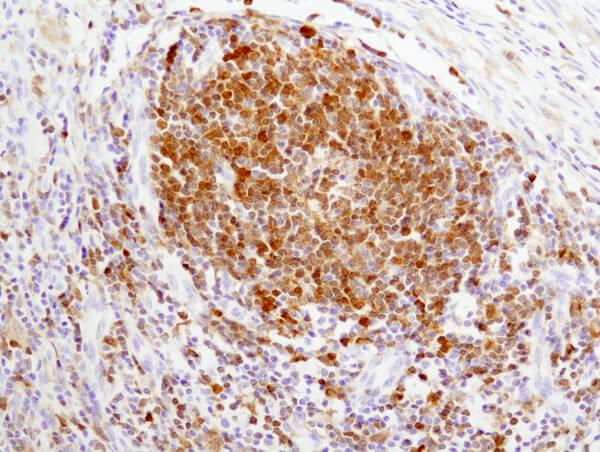
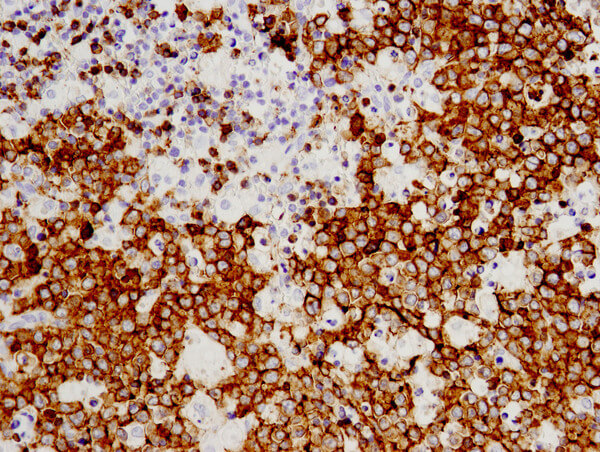
Throughout the various stages of B Cell development and maturation, B Cells express many different markers that can be distinguished by IHC or flow cytometry. Using specific antibodies, stages of individual B Cells can be distinguished from a heterogeneous pool of immune cells. This type of immune cell subtyping is known as immunophenotyping.
CST is your one-stop shop for B Cell immunophenotyping. CST has a wide array of expertly validated antibodies that can distinguish B Cell populations accurately and reproducibly by IHC including:
| B Cell Type | Marker(s) |
|---|---|
| Immature B Cells | CD19, CD34, CD45R |
| Mature B Cells | IgM and CD19 |
| Activated B Cells | CD30 |
| Memory B Cells | CD40 |
| Pan - B Cell | CD79A |