Overview of the Immune System
Introduction
CST supports your immunology research with the highest quality antibodies. Immunology-based research focuses on the components of the human immune system and the possibility of their use to combat various diseases.
You need tools to identify and analyze immune cells and immune signaling to advance your research. CST is proud to produce top of the line antibodies for investigating proteins within the complex signaling pathways of the immune system and to contribute to the international movement to develop better, more efficacious therapeutics.
The immune system is comprised of two broad cellular responses:
- Innate immunity
- Adaptive immunity
Innate Immunity
The innate immune response is your first line of defense against pathogens. It provides a quick response to pathogens by many mechanisms, including cytokine production and complement activation.
The cell types involved in the innate immune response are phagocytic cells: neutrophils, macrophages, natural killer cells, basophils, and others.
As a leader in antibody development, CST has developed a wide array of highly effective antibodies against proteins involved in innate immunity such as the STING, NFκB, and inflammasome signaling pathways.
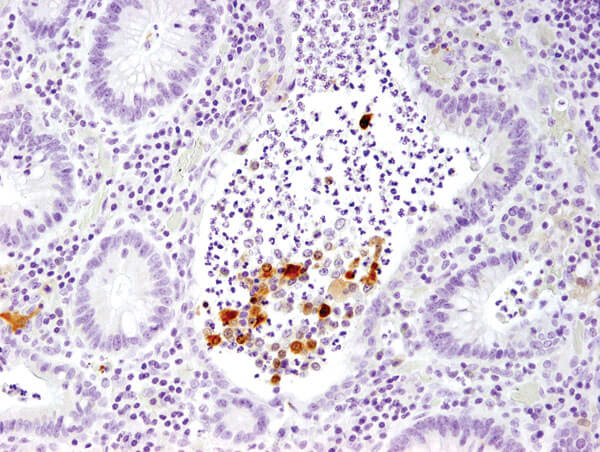
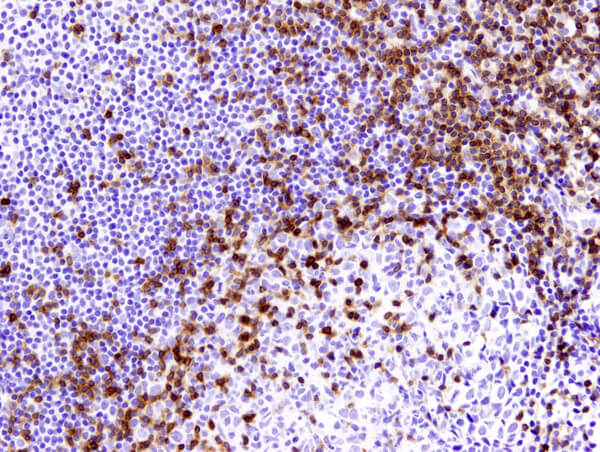
IL-1β (3A6) Mouse mAb #12242: IHC analysis of paraffin-embedded human large intestine (chronic colitis of the colon) #12242.
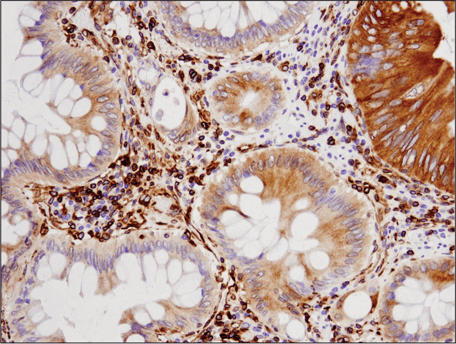
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human colon carcinoma using STING (D2P2F) Rabbit mAb #13647.
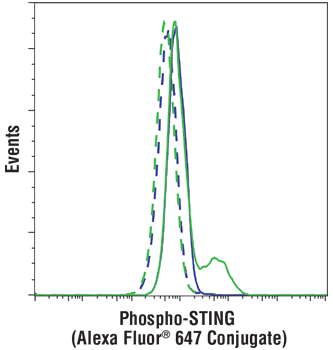
Flow cytometric analysis of THP-1 cells differentiated with TPA #4174 (80 nM, 24 hr), untransfected (blue) or transfected with poly(dA:dT) (5 ug/mL, 3 hr) (green), using Phospho-STING (Ser 366) (D8K6H) Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 647 Conjugate) #43499 (solid lines) or concentration-matched Rabbit (DA1E) mAb IgG XP® Isotype Control (Alexa Fluor® 647 Conjugate) #2985 (dashed lines).
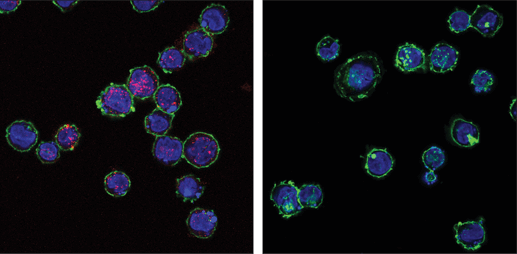
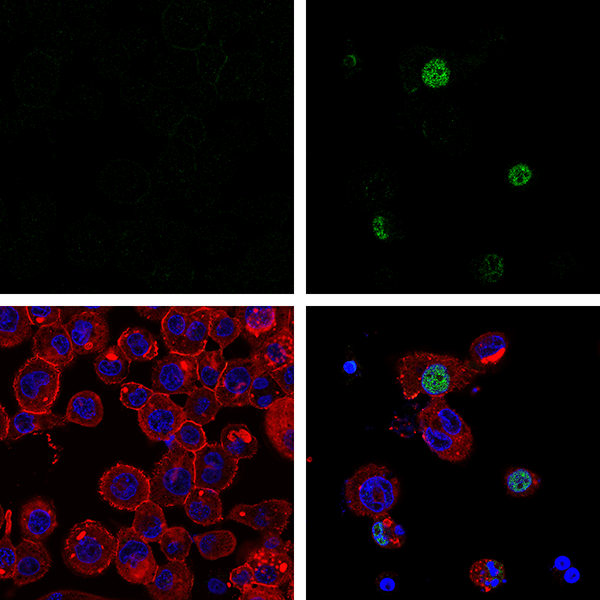
Confocal immunofluorescent analysis of THP-1 cells differentiated with TPA #4174 (80 nM, 16 hr) and then transfected with poly(dA:dT) (5 μg/mL, 3 hr; left) or mock-transfected (right), using Phospho-STING (Ser366) (D8K6H) Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 647 Conjugate) #43499 (red). Actin filaments were labeled with DyLight™ 488 Phalloidin #12935 (green). Blue pseudocolor = Propidium Iodide (PI)/RNase Staining Solution.
Confocal immunofluorescent analysis of THP-1 cells, untransfected (left) or transfected with Poly (I:C) (2.5 μg/ml, 6 hr; right), using Phospho-IRF-3 (Ser386) (E7J8G) XP® Rabbit mAb #37829 (green) and β-Actin (13E5) Rabbit mAb (Alexa Fluor® 647 Conjugate) #8584 (red). Blue = Hoechst 33342 #4082 (fluorescent DNA dye).
Confocal immunofluorescent analysis of HT-29 cells, untransfected (left) or transfected with Poly(I:C) (2.5 μg/ml, 6 hr; right), using IRF-3 (D6I4C) XP® Rabbit mAb #11904 (green). Blue pseudocolor = DRAQ5® #4084 (fluorescent DNA dye).
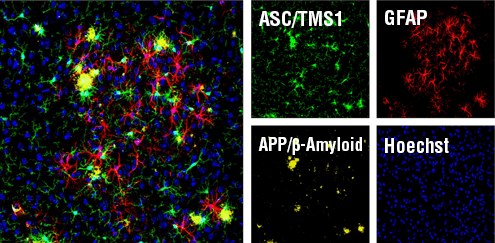
Confocal immunofluorescent analysis of mouse Tg2576 brain which overexpresses mutant human APP695. Sections were first labeled with ASC/TMS1 (D2W8U) Rabbit mAb (Mouse Specific) #67824 (green) and APP/β-Amyloid (NAB228) Mouse mAb #2450 (yellow). After blocking free secondary binding sites with Mouse (G3A1) mAb IgG1 Isotype Control #5415, sections were incubated with GFAP (GA5) Mouse mAb (Alexa Fluor® 647 Conjugate) #3657 (red). Nuclei were labeled with Hoechst 33342 #4082 (blue).
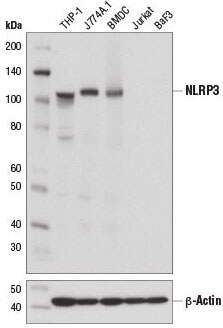
Western blot analysis of extracts from mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDC) and various cell lines using NLRP3 (D4D8T) Rabbit mAb #15101 (upper) and β-Actin (D6A8) Rabbit mAb #8457 (lower).
Adaptive Immunity
The adaptive immune response uses antigen-specific receptors to detect foreign antigens. This is a slow occurrence that results from efforts of T Cells, B cells, and natural killer T Cells. Humoral immunity uses antibodies for detection, whereas cell-mediated immunity uses T Cells to destroy the affected cells.
When the antigen is encountered for the first time, lymphocytes exert the primary immune response. The same cells can “learn” from their experience, so that a subsequent encounter with the same antigen will result in a quicker, secondary immune response.
CST has developed a wide array of highly effective antibodies to label the many proteins involved in the lymphocyte signaling pathways, including the TCR and BCR.
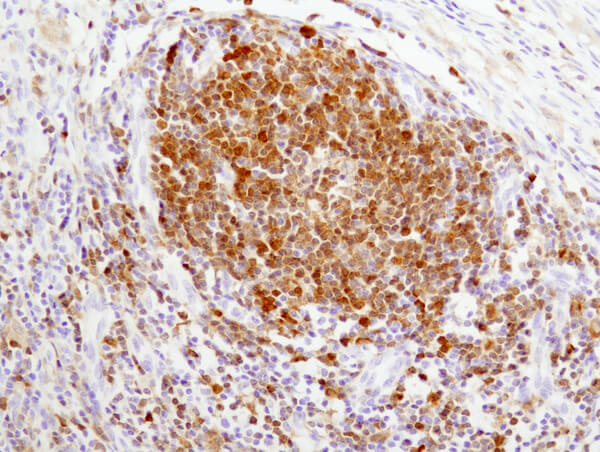
CD3ε (D7A6E™) XP® Rabbit mAb #85061: IHC analysis of paraffin-embedded human tonsil using #85061.
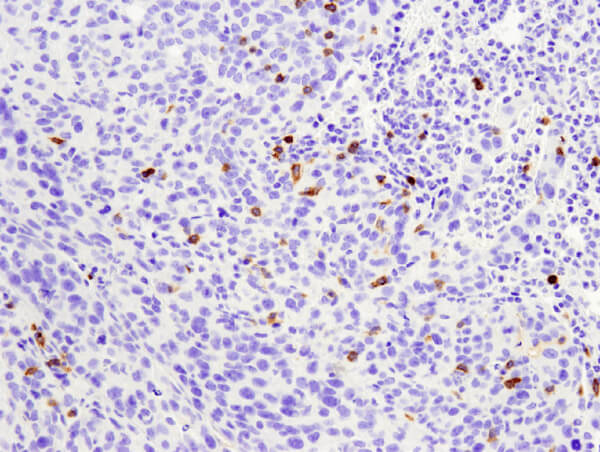
CD4 (D7D2Z) Rabbit mAb #25229: IHC analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse colon using #25229.
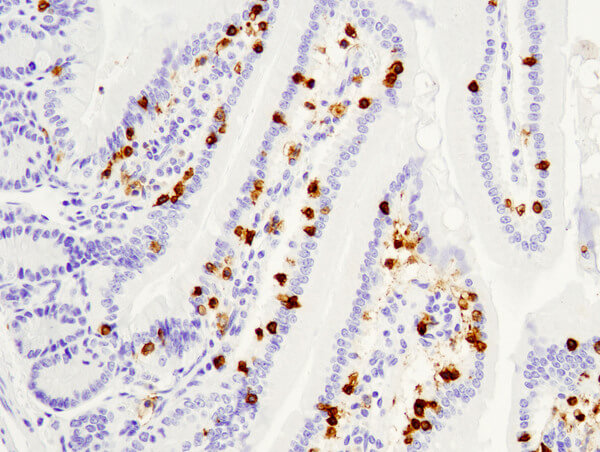
CD8α (D4W2Z) XP® Rabbit mAb (Mouse Specific) #98941: IHC analysis of paraffin-embedded mouse small intestine using #98941.
Immune Cell Signaling
The regulation of immune cells occurs through a number of key signaling pathways. Each pathway is comprised of a complex network of proteins that interact with one another to induce a specific cellular response to stimuli.
In addition to the STING, NFƘB, inflammasome, TCR, and BCR signaling pathways, the JAK/STAT and TLR signaling pathways also play major roles in immune cell signaling.
Syk (D3Z1E) XP® Rabbit mAb #13198: IHC analysis of paraffin-embedded human lymph node using #13198.