Epigenetic regulation, including aberrant DNA methylation and histone modifications, have been linked to Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. However, the exact effects on disease progression are unclear. Brain health is heavily reliant on epigenetic mechanisms, and loss of chromatin dynamics is observed in neurodegenerative diseases. Modifying the environment and targeting sites of potential risk for epigenetic changes are growing areas in the development of therapies against neurodegeneration.
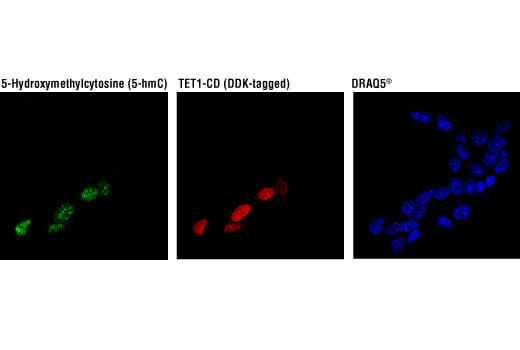
5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) is a novel modified cytosine oxidized from 5-mC (5-methylcytosine) by the Tet protein family. The pattern of 5-hmC throughout development is essential for proper neurodevelopment and neurological function. Dysregulation leads to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease and Huntington’s disease; however, the exact mechanism of action remains to be determined.
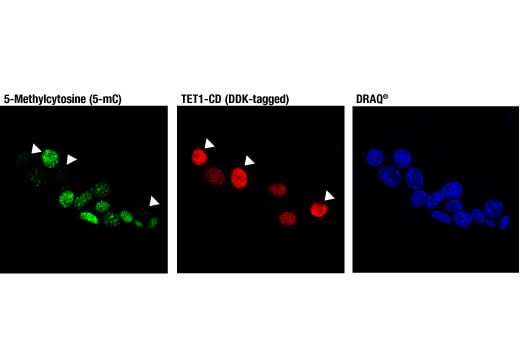
5-methylcytosine (5-mC) is the most common state of cytosine in the brain after the unmodified state. As cells age, total genomic 5-mC content decreases in the brain. Decreased global 5-mC has been observed in Alzheimer’s disease neurons and dysregulation of 5-mC may contribute to progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease.
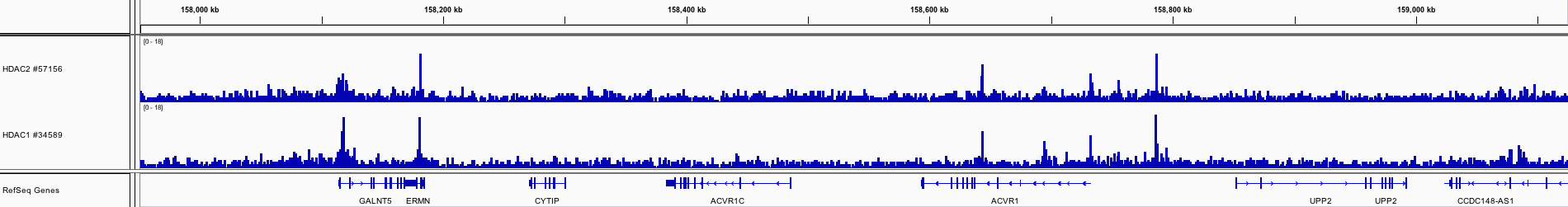
HDAC2 is a class I histone deacetylase that typically leads to gene repression. Deletion of HDAC2 in mouse Alzheimer’s disease models results in improved cognition and decreased amyloid load. Increased HDAC2 expression has also been observed in Alzheimer’s disease patients. HDAC2 is implicated in Huntington’s disease and multiple sclerosis as well.
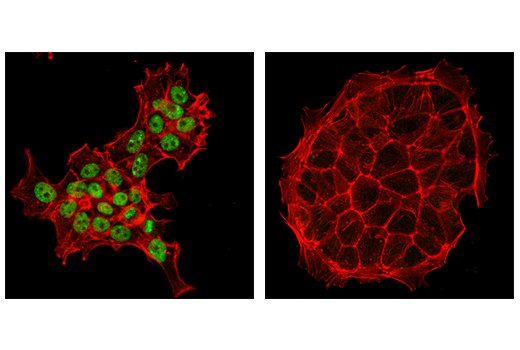
HDAC6 is a class II histone deacetylase with increased expression in the cortex and hippocampus of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. HDAC6 co-localizes with Tau proteins and correlates with Tau phosphorylation. Decreasing HDAC6 levels may result in improved cognition.
p300 is a histone acetyltransferase that plays a role in the chromatin acetylation that is modulated in response to neuronal activity. Neuronal histone acetylation levels are lower in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models, and activation of amyloid precursor protein-dependent signaling results in reduced histone acetyltransferase levels in primary neuronal cultures. p300 also plays a role in Huntington’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.